Data storage and compression
Measurement of the size of computer memories
TIP
A binary digit is referred to as a BIT. 4 bits are 1 NIBBLE. 8 bits are 1 BYTE.
Storage Device
| Measurement | Number of bytes |
|---|---|
| 1 kilobyte(1 KB) | 103 |
| 1 megabyte(1 MB) | 106 |
| 1 gigabyte(1 GB) | 109 |
| 1 terabyte(1 TB) | 1012 |
| 1 petabyte(1 PB) | 1015 |
Computer System
| Measurement | Number of bytes |
|---|---|
| 1 kibibyte(1 KiB) | 210 |
| 1 mebibyte(1 MiB) | 220 |
| 1 gibibyte(1 GiB) | 230 |
| 1 tebibyte(1 TiB) | 240 |
| 1 pebibyte(1 PiB) | 250 |
KB vs KiB
- KB is used in factory and Kib is used in computer system.
Compression types
- Lossless compression reduces the file size without permanent loss of data, e.g. run length encoding (RLE)
- Lossy compression reduces the file size by permanently removing data, e.g. reducing resolution or colour depth, reducing sample rate or resolution.
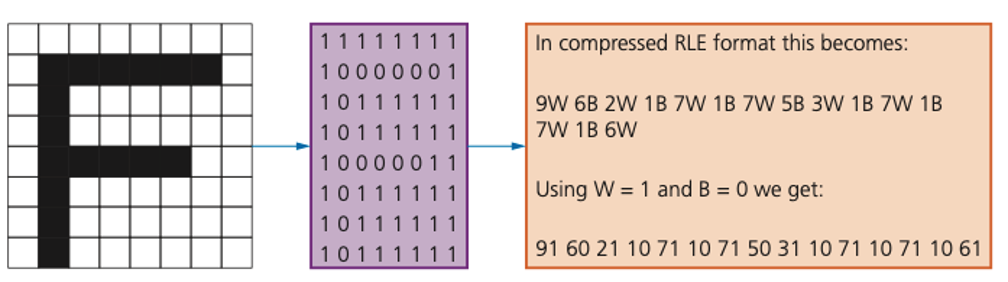
How RLE works
- The original string contains 32 characters and would occupy 32 bytes of storage.
- The coded version contains 18 values and would require 18 bytes of storage.

Also works for images
Audio Compression
MPEG-3 (MP3) uses technology known as audio compression to convert music and other sounds into an MP3 file format which use lossy compression.
Perceptual music shaping removes certain sounds:
- frequencies that are outside the human hearing range
- if two sounds are played at the same time, only the louder one can be heard by the ear, so the softer sound is eliminated.
Image Compression
- When a photographic file is compressed, both the file size and quality of image are reduced.
- A common file format for images is JPEG, which uses lossy file compression.
Compression benefits
- less bandwidth required
- less storage space required
- shorter transmission time